Difference between revisions of "Google banners"
CampMaster (talk | contribs) |
CampMaster (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''This is an introduction to graphical banners and how they can best work through Google | + | '''This is an introduction to graphical banners and how they can best work through Google Ads and its related AdSense system.''' |
== Impressions and clicks == | == Impressions and clicks == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Graphical banners vs. plain text ads == | == Graphical banners vs. plain text ads == | ||
| − | There are plain text | + | There are plain text ads and graphical banners. Plain text ads can be shown on Google's search portal as well as on independent web sites. Plain text ads look all the same and are easily overlooked, much like ads in a newspaper are skipped. While there are exceptions, the lack of visual impact and overuse of plain text ads make them comparatively less effective. Graphical banners have a higher recognision value that can work better to convey a brand beyond Google's search portal. |
== Where are graphical banner ads shown? == | == Where are graphical banner ads shown? == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
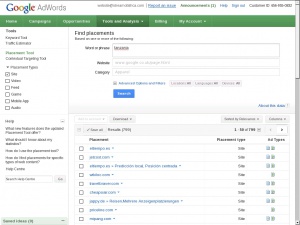
[[File:AdWords placement tool.jpg|thumb|300px|The ''Find placements'' interface in a Google AdWords account.]] | [[File:AdWords placement tool.jpg|thumb|300px|The ''Find placements'' interface in a Google AdWords account.]] | ||
| − | Graphical banners cannot be displayed on Google itself but can appear on a wide variety of web sites and portals whose owners have signed up to display them via Google's AdSense syndication system. Sites on which placements are possible can be found in Google' | + | Graphical banners cannot be displayed on Google itself but can appear on a wide variety of web sites and portals whose owners have signed up to display them via Google's AdSense syndication system. Sites on which placements are possible can be found in Google Ads' Placement Tool. |
== Charge system == | == Charge system == | ||
| − | Graphical | + | Graphical banners and plain text ads work according to a same bidding system within a one and same Google Ads account and are normally charged on a PPC (pay-per-click) basis. Impressions, or simply views, do not cost anything. When clicking an ad on an AdSense connected web site, Google shares its advertising revenue with the owner of the web site where the ad is clicked. |
Advertisers can determine a maximum they are willing to pay each time an ad is clicked as well as in which situations their ads should be shown, whether in plain text on Google itself, or as graphical banners and/or in plain text on various independent web sites. | Advertisers can determine a maximum they are willing to pay each time an ad is clicked as well as in which situations their ads should be shown, whether in plain text on Google itself, or as graphical banners and/or in plain text on various independent web sites. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
Advertisers can manually select which exact sites their ads should be shown on and/or permit Google's system to automatically determine placements based on broadly defined keywords (not recommended) and in which countries and regions their ads should appear. While advertisers can specify their maximum payment p/click and daily budgets, the exact cost p/click is set by an automatic minimum and maximum bidding system, determined by how many advertisers compete for having their ads displayed on certain sites and in various geographical regions. It may cost more to advertise on a particular site for a same ad to be shown to site visitors in California than in Madrid because more advertisers typically place competitive bids for their ads to be shown in the Californian region than in Spain for example. | Advertisers can manually select which exact sites their ads should be shown on and/or permit Google's system to automatically determine placements based on broadly defined keywords (not recommended) and in which countries and regions their ads should appear. While advertisers can specify their maximum payment p/click and daily budgets, the exact cost p/click is set by an automatic minimum and maximum bidding system, determined by how many advertisers compete for having their ads displayed on certain sites and in various geographical regions. It may cost more to advertise on a particular site for a same ad to be shown to site visitors in California than in Madrid because more advertisers typically place competitive bids for their ads to be shown in the Californian region than in Spain for example. | ||
| − | Alternatively, the | + | Alternatively, the system offers CPM (cost p/1000 impressions) based advertising. |
== Geo-targeting by IP range and GPS coordinate == | == Geo-targeting by IP range and GPS coordinate == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
Google's system allows advertisers to configure and target geographical areas, such as individual countries and cities, and depending on the infrastructure of a country's telecom system, specific postal code districts. This applies to plain text ads shown directly on Google as well as graphical banners on AdSense enabled sites. In Google's system, it is done by IP range identification. | Google's system allows advertisers to configure and target geographical areas, such as individual countries and cities, and depending on the infrastructure of a country's telecom system, specific postal code districts. This applies to plain text ads shown directly on Google as well as graphical banners on AdSense enabled sites. In Google's system, it is done by IP range identification. | ||
| − | Geographical targeting surrounding a specified GPS coordinate can be applied to work with mobile devices which are configured to share users individual geo-locations. In short, in cases where Google's geo-detection system knows from where individual site visitors are browsing an AdSense connected site, they can determine to whom an ad should be served as configured by the advertisers within their | + | Geographical targeting surrounding a specified GPS coordinate can be applied to work with mobile devices which are configured to share users individual geo-locations. In short, in cases where Google's geo-detection system knows from where individual site visitors are browsing an AdSense connected site, they can determine to whom an ad should be served as configured by the advertisers within their Google Ads accounts. |
== Provide all available display options == | == Provide all available display options == | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
[[File:Wide skyscraper.gif|border]] | [[File:Wide skyscraper.gif|border]] | ||
| − | == Impressions count == | + | == Impressions that count == |
| − | Ads always receive a much higher proportion of impressions than clicks. A well-designed banner campaign visually connects a brand and | + | Ads always receive a much higher proportion of impressions than clicks. A well-designed banner campaign visually connects a brand and product or service along with its URL by repeated impressions in ways that increase awareness, even when ads are merely noticed and not clicked. <!--In ad-cluttered spaces, this is where plain text AdWords fail to catch attention.--> |
== Animated banners == | == Animated banners == | ||
| − | Animated banners are especially useful for small-screen displays where branding and images do not fit into the available space, e.g. mobile devices. For example, a banner can alternate between company name and logo, slogan, URL and photos. | + | Animated banners are especially useful for small-screen displays where branding and images do not fit into the available space, e.g. mobile devices. For example, a banner can alternate between company name and logo, slogan, URL and product photos. |
| − | Google's system dictates that a cycle of all frames in an animation must complete within 21 seconds, not counting the first (background) frame. Continued and infinite looping is permitted but | + | Google's system dictates that a cycle of all frames in an animation must complete within 21 seconds, not counting the first (background) frame. Continued and infinite looping is permitted but end at the last cycle completed within 21 seconds. <!-- Although Flash-based animations are permitted, they are best avoided due to their lack of support on mobile devices such as Ipads. The most widely supported animation method is therefore the old-fashioned GIF-based animation.--> |
== Maintenance == | == Maintenance == | ||
| − | The | + | The ads system, having evolved over 20 years, has a wide array of ad-delivery configuration options. Setting up a series of ads can easily be done, but running them unchanged is not ideal. Statistical analysis and finding new placement opportunities, being sites that make banner spaces newly available to advertisers, can help deliver maximum result for the available ad-budget. |
__NOEDITSECTION__ | __NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Revision as of 16:18, 20 December 2020
This is an introduction to graphical banners and how they can best work through Google Ads and its related AdSense system.
Contents
- 1 Impressions and clicks
- 2 Graphical banners vs. plain text ads
- 3 Where are graphical banner ads shown?
- 4 Charge system
- 5 Geo-targeting by IP range and GPS coordinate
- 6 Provide all available display options
- 6.1 Banner (468×60 pixels)
- 6.2 Half-page ad (300×600 pixels)
- 6.3 Inline rectangle (300×250 pixels)
- 6.4 Large rectangle (336×280 pixels)
- 6.5 Vertical rectangle (240×400 pixels)
- 6.6 Leaderboard (728×90 pixels)
- 6.7 Mobile leaderboard (320×50 pixels)
- 6.8 Skyscraper (120×600 pixels)
- 6.9 Small square (200×200 pixels)
- 6.10 Square (250×250 pixels)
- 6.11 Wide skyscraper (160×600 pixels)
- 7 Impressions that count
- 8 Animated banners
- 9 Maintenance
Impressions and clicks
In online ad-terminology, an "impression" is when an ad appears in a browser request. The number of impressions is the number of times an ad is shown to users in a given time period. The "clickthrough rate" is the measure of how many times various site visitors have clicked the ad.
Graphical banners vs. plain text ads
There are plain text ads and graphical banners. Plain text ads can be shown on Google's search portal as well as on independent web sites. Plain text ads look all the same and are easily overlooked, much like ads in a newspaper are skipped. While there are exceptions, the lack of visual impact and overuse of plain text ads make them comparatively less effective. Graphical banners have a higher recognision value that can work better to convey a brand beyond Google's search portal.
Where are graphical banner ads shown?
Graphical banners cannot be displayed on Google itself but can appear on a wide variety of web sites and portals whose owners have signed up to display them via Google's AdSense syndication system. Sites on which placements are possible can be found in Google Ads' Placement Tool.
Charge system
Graphical banners and plain text ads work according to a same bidding system within a one and same Google Ads account and are normally charged on a PPC (pay-per-click) basis. Impressions, or simply views, do not cost anything. When clicking an ad on an AdSense connected web site, Google shares its advertising revenue with the owner of the web site where the ad is clicked.
Advertisers can determine a maximum they are willing to pay each time an ad is clicked as well as in which situations their ads should be shown, whether in plain text on Google itself, or as graphical banners and/or in plain text on various independent web sites.
Advertisers can manually select which exact sites their ads should be shown on and/or permit Google's system to automatically determine placements based on broadly defined keywords (not recommended) and in which countries and regions their ads should appear. While advertisers can specify their maximum payment p/click and daily budgets, the exact cost p/click is set by an automatic minimum and maximum bidding system, determined by how many advertisers compete for having their ads displayed on certain sites and in various geographical regions. It may cost more to advertise on a particular site for a same ad to be shown to site visitors in California than in Madrid because more advertisers typically place competitive bids for their ads to be shown in the Californian region than in Spain for example.
Alternatively, the system offers CPM (cost p/1000 impressions) based advertising.
Geo-targeting by IP range and GPS coordinate
Google's system allows advertisers to configure and target geographical areas, such as individual countries and cities, and depending on the infrastructure of a country's telecom system, specific postal code districts. This applies to plain text ads shown directly on Google as well as graphical banners on AdSense enabled sites. In Google's system, it is done by IP range identification.
Geographical targeting surrounding a specified GPS coordinate can be applied to work with mobile devices which are configured to share users individual geo-locations. In short, in cases where Google's geo-detection system knows from where individual site visitors are browsing an AdSense connected site, they can determine to whom an ad should be served as configured by the advertisers within their Google Ads accounts.
Provide all available display options
There are currently 20 possible display sizes. The available size for placement on any given site is determined solely by the preferences of the individual web site publisher, not by the advertiser. To ensure a maximum reach for campaigns, multiple display options can be catered for by making graphical banners available in several available sizes. Below are the 11 common sizes.
Banner (468×60 pixels)
Half-page ad (300×600 pixels)
Inline rectangle (300×250 pixels)
Large rectangle (336×280 pixels)
Vertical rectangle (240×400 pixels)
Leaderboard (728×90 pixels)
Mobile leaderboard (320×50 pixels)
Skyscraper (120×600 pixels)
Small square (200×200 pixels)
Square (250×250 pixels)
Wide skyscraper (160×600 pixels)
Impressions that count
Ads always receive a much higher proportion of impressions than clicks. A well-designed banner campaign visually connects a brand and product or service along with its URL by repeated impressions in ways that increase awareness, even when ads are merely noticed and not clicked.
Animated banners
Animated banners are especially useful for small-screen displays where branding and images do not fit into the available space, e.g. mobile devices. For example, a banner can alternate between company name and logo, slogan, URL and product photos.
Google's system dictates that a cycle of all frames in an animation must complete within 21 seconds, not counting the first (background) frame. Continued and infinite looping is permitted but end at the last cycle completed within 21 seconds.
Maintenance
The ads system, having evolved over 20 years, has a wide array of ad-delivery configuration options. Setting up a series of ads can easily be done, but running them unchanged is not ideal. Statistical analysis and finding new placement opportunities, being sites that make banner spaces newly available to advertisers, can help deliver maximum result for the available ad-budget.